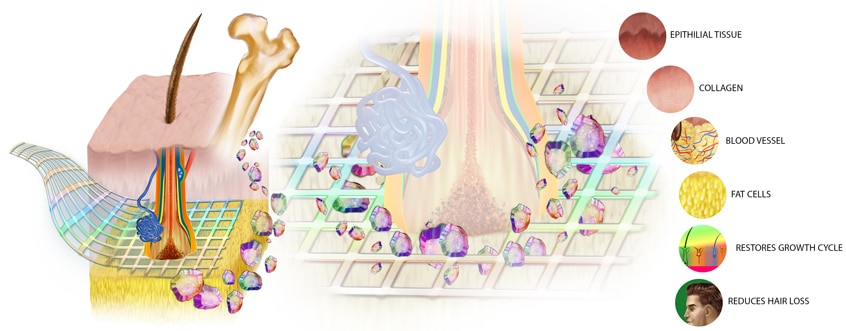
The Extracellular Matrix (ECM) is a complex mixture of nonliving material that surrounds the cells, providing structural and biochemical support to every system in the body. The structural support differs depending on the type of cells it supports; thus the structural support for the brain is different than for the skeletal system.
The ECM is mainly made of carbohydrates and protein. The consistency of these carbohydrates and proteins also varies for each system, which results in differences in the stiffness and elasticity of each system’s ECM. Therefore, the bone ECM is stronger than that of other body systems.
The medical use of ECM is in tissue regeneration. ECM helps the cells to repair and grow, at the same time inhibiting the immune response to injury, which leads to scarring. ECM of the skeletal systems helps stem cells differentiate to support bone tissue, while ECM of soft tissue will help repair and regenerate the body’s soft tissue.